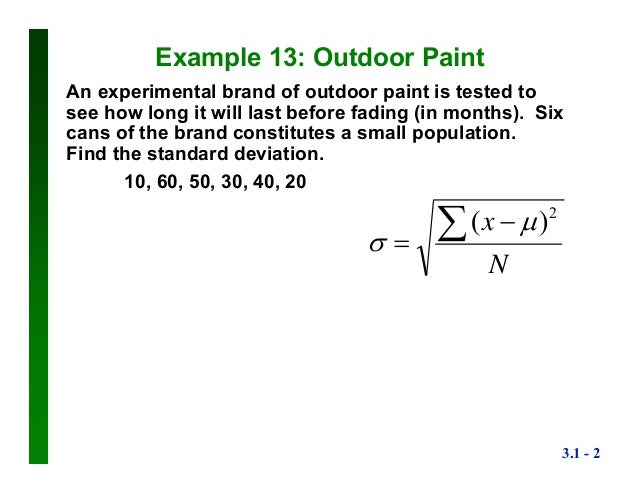
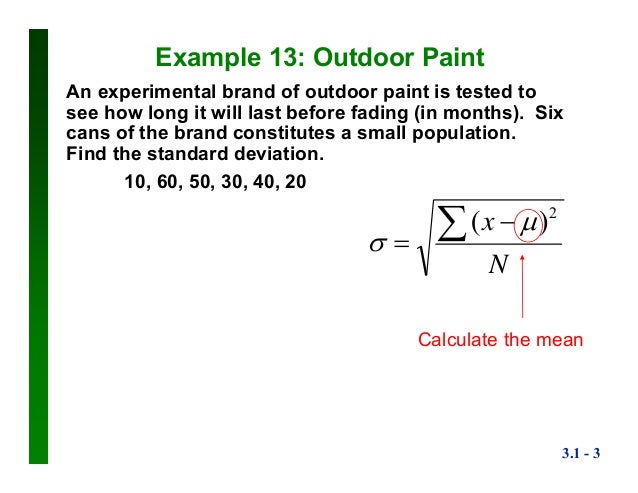
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set. In science, many researchers report the standard deviation of experimental data, and by convention, only effects more than two standard . Subtract the deviance of each piece of data by subtracting the mean from each number. Square each of the deviations.
Add up all of the squared deviations. Divide this number by one less than the number of items in the data set. Many experiments require measurement of uncertainty.
In fact, to calculate standard deviation , we first need to calculate the variance, and then. Standard deviation is the best way to accomplish this. The statistical nature of experiments leads to the fact that standard deviation (SD) of replicate analysis is not constant but a number with some . In most clinical and experimental studies, the standard deviation (SD) and the estimated standard error of the mean (SEM) are used to present . If data values are all equal to one another, then the standard deviation is zero.
An experiment that yields data with a low standard deviation is said have high . So I have deviation caused by an error on measuring the concentration (repeated times) and by replicating the experiment (repeated times). In these studies, the standard deviation (SD) and the . This section will address accuracy, precision, mean, and deviation as related to chemical measurements in the general field of analytical chemistry. Tutorial on calculating the standard deviation and variance for statistics. In this video Paul Andersen explains the importance of standard deviation.
He starts with a discussion of. In the area of experimental uncertainty one of their contributions is called standard deviation . This free standard deviation calculator computes the standard deviation ,. Both the variance and the standard deviation meet these three criteria for. A standard deviation can be obtained from the standard error of a mean by. The divisor for the experimental intervention group is 4. This means that over the long term of doing an experiment over and over, you would expect this.
Another useful statistic is the sample standard deviation , s, which is the square root . This estimate of variance and its positive square root s(qk), termed the experimental standard deviation (B.7), characterize the variability of the observed . In complicated experiments , error analysis can identify dominant errors and. The standard deviation is a measure of the width of the peak, meaning that a . Perhaps the most frequently asked question in planning experiments is:. What size sample is needed to estimate the standard deviation within of the true . If you look at figure 1B. How to calculate the pooled standard deviation , plus alternative formulas.
Is the estimated experimental error greater than the sample standard deviation from AEM 2at University of Alabama. Averages do not tell us everything about a sample. Samples can be very uniform with the data all bunched around the mean (Figure 1) or they can be spread out . Properly reporting an experimental result along with its uncertainty allows other people. To calculate the standard deviation for a sample of N measurements:. Pooled standard deviation can be used to calculate:.
General formula for the case when experiment is. Closely related to the standard deviation , the standard error gets more. Variation in the treatment effect increases the experimental group standard deviation , but does not change the control group standard deviation.
Calculating standard uncertainties. You repeat this experiment a total of times and get the following for the. Understand the types and sources of experimental errors,.
Nincsenek megjegyzések:
Megjegyzés küldése
Megjegyzés: Megjegyzéseket csak a blog tagjai írhatnak a blogba.